May 27, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowC-Aware IDE Compilers are able to read data streamed to a PC where it can be plotted in real time using the IDE's Serial Input/Output Monitor. From the 'Tools' ribbon launch the Serial Input/Output Monitor program, which is a powerful and easy-to-use serial port terminal program. Serial Input/Output Monitor allows the user to easily connect to a serial COM port or telnet port.

The Data Graph in the screenshot above was generated using the following code:
#include "e3mini.h"
#define GRAPH_TITLE "Sin Graph"
#define GRAPH_SERIES1_TITLE "Sin"
#define GRAPH_SERIES2_TITLE "Cos"
#define GRAPH_X_MIN "0"
#define GRAPH_X_MAX "719"
#define GRAPH_Y_MIN "-1"
#define GRAPH_Y_MAX "1"
#include <graph_siow.h>
#include <math.h>
void main (void) {
init_graph();
for(int16 z = 0; z < 720; z++) { graph_points2(sin((z*3.14)/180), cos((z*3.14)/180)); } }
Serial Input/Output Monitor also offers advanced features such as file transfer, microcontroller boot-loading, macros, logging, and graphing. Devices capable of outputting comma delimited ASCII data through a USB or RS-232 port can have their output displayed in real-time on a graph from within the IDE. The device can be connected directly to the PC's USB or serial port; no debugger or other hardware is required. This capability is especially useful when debugging data acquisition systems and sensors, motion control systems, etc.
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | July 10, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowThe CCS C Compiler supports C++ like function overloading. Function overloading allows the user to develop two functions with the same name but have different parameters or return types. Recently the CCS C Compiler updated the function overloading to distinguish between RAM and ROM pointers as well. This is useful on the PIC® MCU which uses the Harvard architecture, meaning accessing the RAM and ROM is different. Since accessing RAM and ROM is different, the compiler needs to know which one the user is accessing so it can use the proper method.
Here is a simple example of function overloading using ROM and RAM pointers:
int1 Checksum(rom char* pRom, int hashCompare) { int hash = HashCalculateRom(pRom); if(hash == hashCompare) return 1; else return 0; }
int1 Checksum(char* pRam, int hashCompare) { int hash = HashCalculate(pRam); if(hash == hashCompare) return 1; else return 0; }
SetSavedString((rom char*) "Hello World");
SetSavedString((char*) "foo bar"); has two functions, one for handling ROM pointers and one for handling RAM pointers. In the CCS C Compiler the 'rom' keyword specifies the ROM flash memory, if this is not specified the CCS C Compiler will use RAM. When Checksum() is called with the "Hello World" as a 'rom char*' It passes the pointer to the HashCalculateRom() method, that calculates the hash value for the pointer and compares it to the hashCompare value passed in by the user. The same is done when "foo bar" is passed in as a 'char*' but it passes the pointer into the HashCalculate() method that is used for RAM locations. If the calculated hash matches the user input hashCompare, then Checksum() returns '1', otherwise it returns '0'.
Here is a more complex example of function overloading based on ROM and RAM pointers:
struct { union { rom char* pRom; char* pRam; }; int1 isRom; } savedString;
void SetSavedString(rom char* pRom) { savedString.pRom = pRom; savedString.isRom = TRUE; }
void SetSavedString(char* pRam) { savedString.pRam = pRam; savedString.isRom = FALSE; }
void PrintSavedString(void) { if(savedString.isRom) printf("%s", savedString.pRom); else printf("%s", savedString.pRam); }
SetSavedString((rom char*)"Hello World");
SetSavedString((char*) "foo bar"); saves a (char*) or (rom char*) depending on what was passed in by the user to memory, and sets a flag denoting the type of pointer that is being used. The PrintSavedString() checks the flag to select the proper pointer, and prints the string.
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | July 10, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowThe CCS compiler addressmod() feature allows you to define custom memory spaces. This new function that replaces the older typemod() function now makes it easy to use the shared bank memory in many processors for specific variables your code uses. addressmod() allows for faster access to those variables.
addressmod(), supported in the CCS C Compiler, provides embedded C developers a way of declaring variable types with many custom parameters like specific read and write functions or memory ranges. This is useful in embedded applications because there are often several types of memory available in a design that need to be accessed, like RAM, ROM, EEPROM, Flash, and even LCDs. This article highlights a few details of addressmod(), for full details refer to the CCS C Compiler manual.
Recently the CCS C Compiler added a new optional parameters to addressmod() called 'share'. If this option is defined as TRUE, the CCS C Compiler will allow the addressmod() declared variable type to also be used by other variables but the addressmod() declared variables will have to be allocated in that region first. This is useful for the access of bank memory described above, as a developer may want to have some variables allocated in this region but leave it available for the compiler to use the remaining space for other variables.
The usage is:
addressmod(name, read_function, write_function, start_address, end_address, share);
Here is an example:
#if defined(__PCM__)
addressmod(near, , , 0x70, 0x76, TRUE); #elif defined(__PCH__)
addressmod(near, , , 0x20, 0x5f, TRUE); #elif defined(__PCD__)
addressmod(near, , , 0x1000, 0x1fff, TRUE); #endif
near char flags;
char option;
The addressmod() code above can be copied and pasted into your projects to define a 'near' memory region that uses the PIC ® MCU access bank.
'near' is an addressmod() created memory region that sits in the PIC ® MCU access bank. Pre-processor #if / #else is used to make a 'near' for every applicable PIC ® MCU architecture. Since the 'share' flag in addressmod() is set TRUE, the compiler will make this memory region available for general use once 'near' variables have been allocated. The variable 'flags' uses the 'near' memory region, meaning 'flags' is placed in the access bank. The 'option' variable does not have a memory region specified, so the compiler will use any RAM region available. If the user allocated more variables than can be saved in the 'near' region, the compiler will generate an 'Out of RAM' error message.
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | August 12, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowCCS, Inc. will be presenting at the 18th annual Microchip's MASTERs Conference this August 20-23 in Phoenix, AZ. The focus this year is The Internet of Things which is ideal to showcase our new Wireless Sensor Control App using the CCS IDE which allow users to easily create a Smart Device App that pairs to your PIC® for reading field data on the fly. Also, our EZ Web Lynx Modules enable you create the Internet of Things, very quickly, using either a Wi-Fi or Ethernet Module add-on and HTML programming to get your product to the Internet.
Darren Rook, CCS Lead Engineer, will be teaching a class on converting Assembly Code to C using the CCS IDE. Attendees of the Using the CCS C compiler for painless migration from Assembly to C Class will learn how to convert Assembly to C using a sample Assembly application for the PIC16F1XXX. Darren will demonstrate in a step-by-step fashion how to implement the necessary constructs in C. Techniques will be covered specifically for the CCS C compiler. For the hands-on portion of the course, participants will experience the speed and ease of developing applications from scratch, using the CCS C Compiler. Also covered will be the use of the application Wizard, basic IDE use, programming concepts and advanced debugging techniques, as well as new features of the IDE.
For more information on the conference, to register, or to sign up for the CCS class, please visit the Microchip MASTERs website.
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC® MCU and dsPIC® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC® MCU, MPLAB® IDE, MPLAB® ICD2, MPLAB® ICD3 and dsPIC® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | September 24, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowThe CCS C-Aware IDE's Files navigation panel and file tabs have been improved to enhance viewing of large project files. The File tab in the navigation panel now adds subfolders for project files that are not in the main project directory. Simply collapse any folder to hide extraneous files for viewing. This new function is especially useful for projects that have files split into multiple directories which makes it easier to find the files you are searching for.
All open file tabs maybe viewed in multiple rows, making it handy for keeping many files open at the same time. No longer is it necessary to tab in succession until a file is found. This feature can be turned on under 'Options' > 'IDE' > 'General' then check 'File Tabs Span Multiple Rows' option.

Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | September 24, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowThe TCP/IP Project Wizard, within any of the CCS C-Aware IDE Compilers, now enable HTTP Client applications in a snap! Get your Internet ready project started quickly, in the Project Wizard, by using an Internet capable PIC® MCU and setting up the device as an HTTP Client. This frees the device to communicate with an HTTP Server over a Network or Internet.
Kickoff your TCP/IP project with just 3 simple steps: First, click over to the HTTP Client tab to specify the IP address or hostname of the server. Second, designate a URL, or file, for access with an additional custom header - if needed. Third, enable CGI format and a CGI key/value pair to send in the GET/POST request - if required. Setup is now complete! The Project Wizard will now generate a base code framework with helpful 'TODOs'. These 'TODOs' mark where specified tasks need to be handled in the project code. The TCP/IP stack, automatically included in the project, is tailored to the options you have chosen through this Project Wizard. It's that simple!
Sample Project Code:
while(TRUE)
{
... ... ... ...
if (0) // todo: specify action condition, like a button press
{ g_MyHttpSending = TRUE;
MyHttpSend(); }
else if (!HttpClientIsBusy() && g_MyHttpSending)
{ g_MyHttpSending = FALSE;
// todo: if you want to see the pass/fail of the request,
// use HttpClientGetResult()
// todo: if you want to see the data read from the server,
// look at the g_MyHttpResponse[] string }
... ... ... ...
} 
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | October 21, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowCCS has recently added a Project History tool to the C-Aware IDE for PIC® MCUs. This new tool provides a simple UI ideal for: tracking file changes, additions to a project, comparing files, and managing file history - automatically saved by the IDE. Project History is accessible from the 'View' ribbon, under 'Project', within in the IDE.
Selecting Files, Creating Copies, and Deleting Copies.
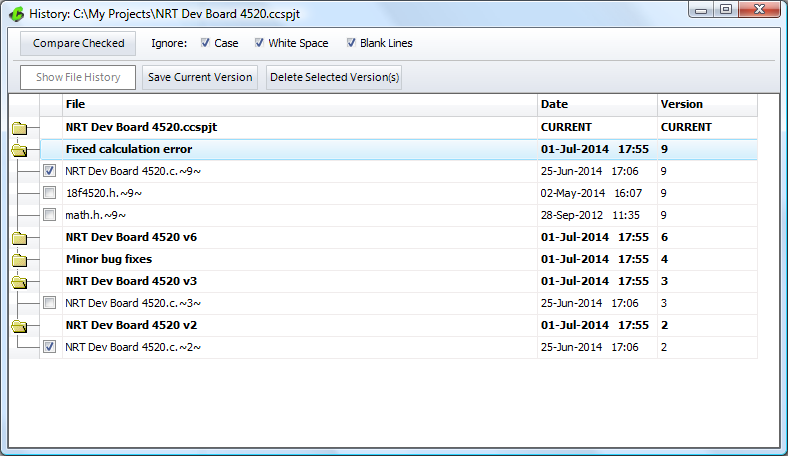
In the Project History tool, by expanding a project version, it displays all of the saved files in that version. Selecting files for comparison, or viewing individual file histories, can be accomplished from here. Clicking the 'Save Current Version' button makes a copy of all current project files and adds it to the version list. These newly copied versions cannot be overwritten by the IDE's History option. The copies can only be deleted through the Project History tool by selecting these versions and clicking the 'Delete Selected Versions' button.
Changing the name of a Project
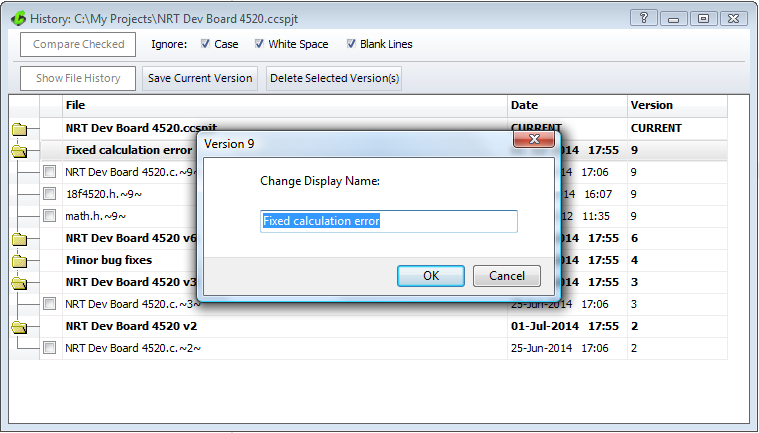
To change the name of a project version, through the Project History tool, double-click on the version name from the list of projects. This will bring up a dialog to change the name in the textfield. By clicking 'OK' the new name is displayed in the list of projects for easier identification of your saved project versions.
Viewing Autosaved Files and Locking or Unlocking Files.
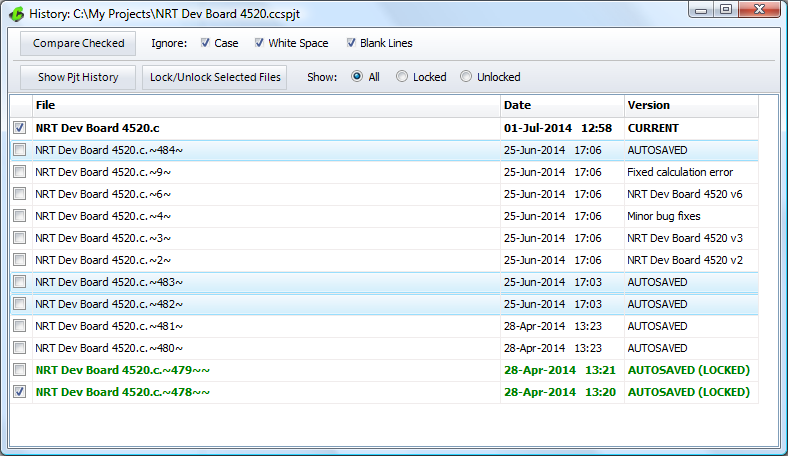
By default the IDE is set up to automatically keep history of files edited within the editor. The new Project History tool allows for viewing these 'autosaved' files. To do this, simply select a file and click the 'Show File History' button. Now all versions of the selected file, that were automatically saved, will be viewable. Also viewable are the project history versions saved by manually saving the project.
Now, through the Project History tool, there is the ability to 'Lock' or 'Unlock' files that were automatically saved. Locking files prevents them from being overwritten when auto-save takes place. The 'Auto-Save' feature can be managed in the 'History' section of 'IDE Options'. Here the maximum number of files saved when auto-saving can be set as well. Once the IDE reaches the maximum number of files saved, older versions will be overwrited - unless they are locked.
Show File History
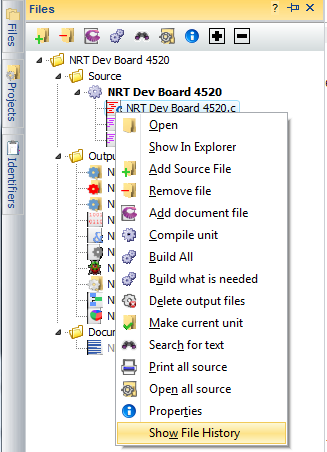 | 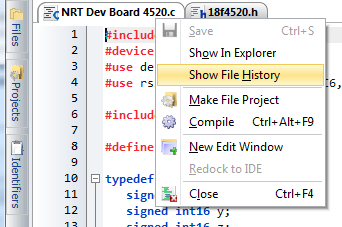 |
Project History has been integrated into the File Tab menu and the Left Navigation panel. Simply right-click on the File Tab, or right-click on the file in the Navigation Panel. This right-click menu will present an option to 'Show File History'. From here the ' AUTOSAVED' files and ability to 'Lock' and 'Unlock' selected files will be made available.
Easily Compare File Versions
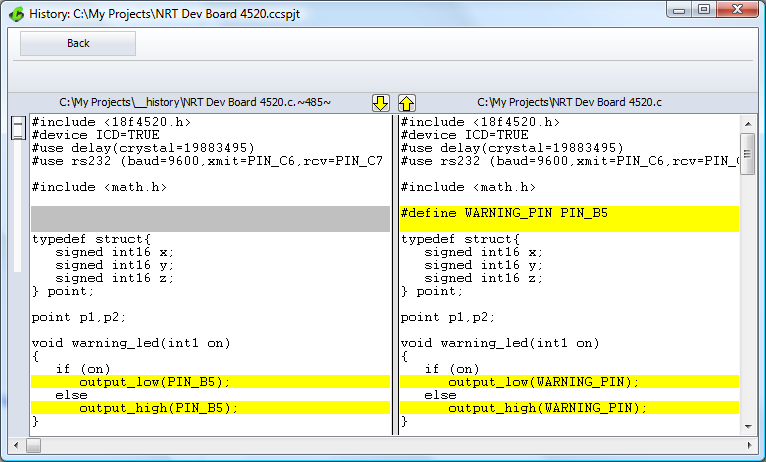
The file compare tool has been built into Project History for quick and simple comparing of file versions. You can compare file versions by checking the boxes next to the two files and clicking 'Compare Checked'. This allows you to see exactly what has changed between the two versions without having to leave the tool!
Give it a try today!
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | October 21, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowMark Siegesmund, founder of CCS and creator of the CCS C Compiler for PIC® MCUs, has recently published a new book: Embedded C Programming - Techniques and Applications of C and PIC® MCUs. The intended audience are those without formal training in C or those lacking experience programming a microcontroller. This is an excellent text for Electrical Engineers and others who need to get up to speed on the C language. This book provides a hands-on introductory course on concepts of C programming using a PIC® microcontroller and the CCS C compiler. Through a project-based approach, this book provides an easy to understand method of learning the correct and efficient practices to program a PIC® microcontroller in the C language. Principles of C programming are introduced gradually, building on skill sets and knowledge. Early chapters emphasize the understanding of C language through experience and exercises, while the latter half of the book covers the PIC® microcontroller, its peripherals, and how to use those peripherals from within C in great detail.
This book demonstrates the programming methodology and tools used by most professionals in embedded design. The reader will be able to apply what they learn to real-life embedded applications. Providing a step-by-step guide to the subject matter, this book will encourage you to alter, expand, and customize code for use in your own projects.
Key features include:
- A complete introduction to C programming using PIC® microcontrollers, with a focus on real-world applications, programming methodology and tools
- Each chapter includes code examples, exercises and a quiz.
- C code project examples, tables, graphs, charts, references, photographs, schematic diagrams, flow charts and compiler compatibility notes to channel your knowledge into real-world examples.
- Includes Single-Chip C compiler software with full documentation.
- Online educator materials available from publisher.
- Low-cost companion hardware available.
To Purchase or For More Information from Amazon
About the Author:
Mark Siegesmund is a software engineer with over 30 years of experience in embedded sytems within the military, industrial and commercial sectors. He is the founder of Custom Computer Services, Inc. (CCS). CCS specializes in embedded software and hardware, offering development tools for Microchip MCUs and DSCs, as well as a line of embedded Ethernet development tools EZ Web Lynx.
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | December 4, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowThe CCS C Compiler pulse width modulation (PWM) library (#use pwm()) has been improved to provide software, bit-banged PWM control over any I/O pin without limitations. This new feature provides accurate PWM as well as customizable setup for period, frequency, duty cycle, and more... There are three unique features that make it versatile; setting it apart from using the hardware PWM peripheral:
- The ability to assign multiple output pins to the same signal
- The ability to explicitly set logic level of the output (or outputs) when the PWM is inactive
- The tristate operating mode
Setting up the software PWM is simple and easy. Any desired options for duty cycle, period, frequency, etc. may be set while only using one line of code. Below is an example that illustrates the setup of a typical PWM with two outputs, a frequency of 1 kHz, and a duty cycle of 75%.
#use pwm(output=pin_a4, output=pin_b3, timer=1, frequency=1kHz, duty=75)
The signal will now output on both pins A4 and B3. Adding or removing more output pins is as simple as adding or removing output=X options.
Once running, the function pwm_set_duty_percent() may be used to change duty cycle. A stream identifier may be used in the #use pwm(), and other PWM functions, which allow multiple PWM pins to operate at the same time.
When disabled, the output pins of the Software PWM are capable of holding specific logic levels: high, low, and input. These options make the software PWM dependable even while disabled. The option to designate a specific disable level, may be added to the setup. Below is an example that designates a disable level using the PWM which was set up previously.
#use pwm(output=pin_a4, output=pin_b3, timer=1, frequency=1 kHz, duty=75, disable_level=low)
Now, whenever the built-in function pwm_off() is called, both pins a4 and b3 will be driven low.
An alternate operating mode for the software PWM is the tristate mode. In tristate mode, the compiler will force all output pins, associated with the PWM signal, to become inputs during the duty high time - instead of forcing them high. Activating tristate mode requires that only one simple option, ' tristate', be added to the setup.
The CCS C-Aware IDE will display a message indicating the output of the software PWM just as it does with hardware PWM. This feature is useful since the compiler may not be able to hit the exact frequency desired due to speed or processing limits of the target microcontoller used. Using the code from the examples above, the following is the message displayed by the IDE at compile time as well as the actual output as observed using a logic analyzer:
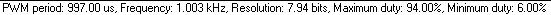 IDE message containing information on the Software PWM output
IDE message containing information on the Software PWM output
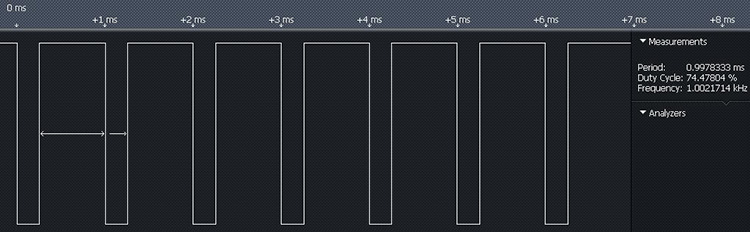 The actual output of the Software PWM
The actual output of the Software PWM
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. | December 4, 2014  Expand to read article below Expand to read article belowCCS C-Aware IDE now includes the EZ App Lynx library (#include <EZApp.c>). Quickly create a Bluetooth® wireless sensor, or controller, that may be viewed or managed on a paired mobile device - using the EZ App Lynx Android App. The free EZ App Lynx Library was created to shorten the design time for smart Bluetooth® app development. With EZ App Lynx, and no required hardware or software expertise, the library removes the barriers to entry for smartphone app developers who want to take advantage of a growing number of Bluetooth® enabled smartphones and tablets. The new library allows for any GUI, on the App, to be created at run time from a PIC® program. The library offers many useful sensor interface components which allow for: Status Bars, Gas Gauges, Sliders, Buttons, Text Fields, and More...
EZ App Lynx Library Features and Advantages:
- NO App design knowledge required
- Source code libraries included with all CCS C Compilers
- Included with maintenance update download
EZ App Lynx App:
- Available for Android in Google Play Store. (iOS available soon)
- Build your own EZ App Lynx App in minutes with simple C library calls on the PIC®
- Quick and easy prototyping
How It Works:
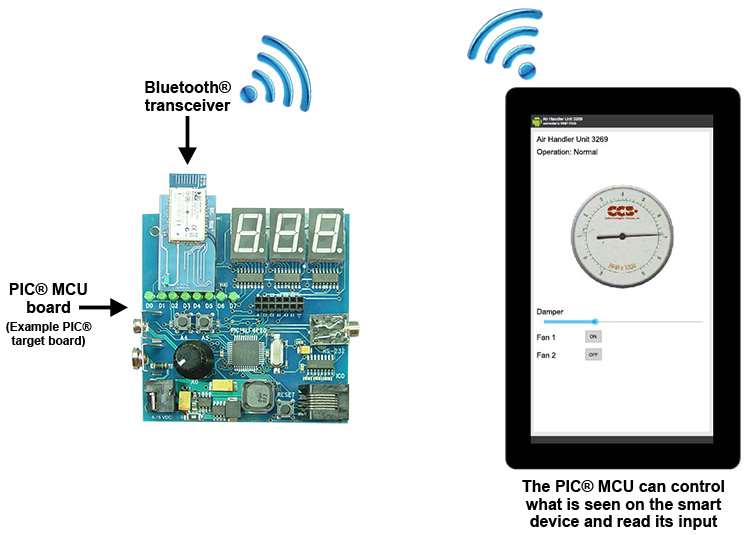
To make use of the EZ App Lynx library and app you'll need a prototyping board with PIC ® MCU and a Bluetooth ® module with SPP - both sold separately. Attach the module to board, and from within the IDE insert the following example code:
--
#include "main.h"
#include <EZApp.c>
void main(void)
{
ezapp_field_index_t strIndex, rpmIndex, damperIndex, fan1Index, fan2Index;
rom char* title = "Air Handler Unit 3269";
HW_INIT();
EZAppInit();
EZAppSetTitleROM(title);
EZAppSetValueStringROM(EZAppAddFieldString(), title);
strIndex = EZAppAddFieldString();
rpmIndex = EZAppAddFieldAnalogValue(
(rom char *)"RPM X 1000", //header
EZAPP_ANALOG_TYPE_SLIDER, //display type
1024, //max value
9 //scaling );
damperIndex = EZAppAddFieldAnalogValue(
(rom char *)"DAMPER", //header
EZAPP_ANALOG_TYPE_SLIDER, //display type
1023 //max value );
fan1Index = EZAppAddFieldButtonTwoState(
(rom char*)"Fan 1", //header
(rom char*)"Off\tOn" //strings that go in button );
fan2Index = EZAppAddFieldButtonTwoState(
(rom char*)"Fan 2", //header
(rom char*)"Off\tOn" //strings that go in button );
for(;;)
{
EZAppTask();
if (IsFailure())
{
EZAppSetValueStringROM(strIndex, (rom char*)"Operation: Failure"); }
else
{
EZAppSetValueStringROM(strIndex, (rom char*)"Operation: Normal"); }
EZAppSetValue(rpmIndex, read_adc());
if (EZAppGetKbhit(damperIndex))
SetDamper(EZAppGetValue(damperIndex));
if (EZAppGetKbhit(fan1Index))
SetFan1(EZAppGetValue(fan1Index));
if (EZAppGetKbhit(fan2Index))
SetFan2(EZAppGetValue(fan2Index)); } } --
The new EZ App Lynx Library is included for all new or existing IDE customers. To update your IDE Compiler to the latest version and receive the EZ App Lynx Library click here. To upgrade to a C-Aware IDE compiler click here or call sales. The EZ App Lynx can be used as a reference design and development platform for a variety of smart Bluetooth ® sensors. So get started on your Bluetooth ® app development today!
Like us on Facebook. Follow us on Twitter.
About CCS:
CCS is a leading worldwide supplier of embedded software development tools that enable companies to develop premium products based on Microchip PIC ® MCU and dsPIC ® DSC devices. Complete proven tool chains from CCS include a code optimizing C compiler, application specific hardware platforms and software development kits. CCS' products accelerate development of energy saving industrial automation, wireless and wired communication, automotive, medical device and consumer product applications. Established in 1992, CCS is a Microchip Premier 3rd Party Partner. For more information, please visit http://www.ccsinfo.com.
PIC ® MCU, MPLAB ® IDE, MPLAB ® ICD2, MPLAB ® ICD3 and dsPIC ® are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. in the U.S. and other countries.
The Bluetooth ® word mark and logos are registered trademarks owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc. and any use of such marks by Bluegiga Technologies is under license. Other trademarks and trade names are those of their respective owners. |
|
